Texas Gov. Abbott Backs $500M CesiumAstro HQ in Bee Cave
A $500 million aerospace investment is set to bring 500 high-tech jobs to Central Texas through the construction of a specialized satellite production facility.
Texas Governor Greg Abbott confirmed on January 14, 2026, that CesiumAstro will relocate its global headquarters and advanced manufacturing operations to Bee Cave, Texas.
The project represents a capital investment exceeding $500 million and is expected to expand the company’s workforce by 500 employees over the next five years.
The development transforms a site previously approved for a large distribution warehouse into a secure, high-precision manufacturing campus focused on software-defined satellite communications hardware.
At full capacity, the Bee Cave facility will serve as CesiumAstro’s primary center for building phased-array communication systems used across defense, civil, and commercial space missions.
The move also marks a defining early win for the Texas Space Commission, which was created to diversify Texas’ space economy beyond traditional launch and mission-control hubs such as Houston.
State officials view the project as a strategic step toward reshoring the domestic production of sensitive satellite technologies and reducing reliance on foreign supply chains for critical aerospace and defense components.
Who is CesiumAstro?
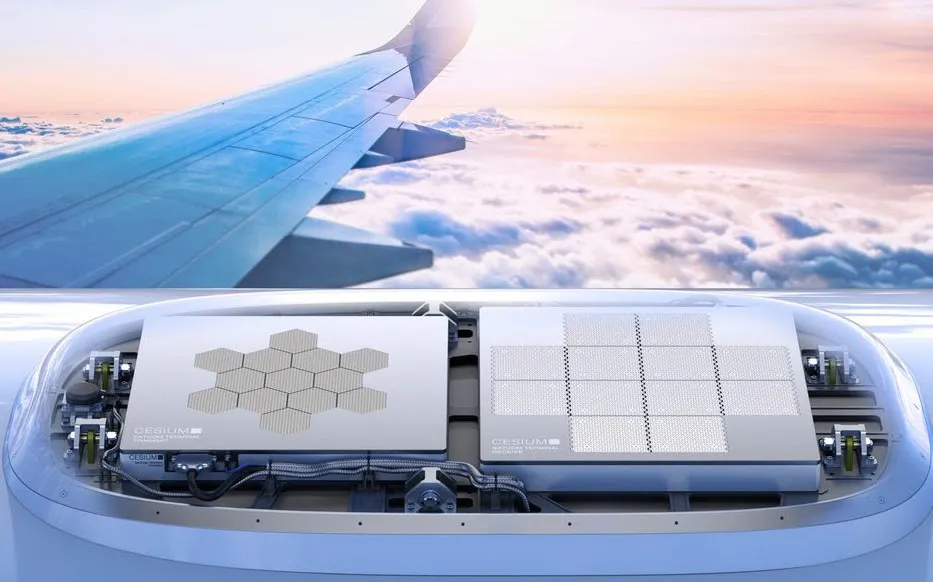
Founded to rethink how satellites communicate, CesiumAstro specializes in software-defined, reconfigurable phased-array systems that can operate across space, airborne, maritime, and terrestrial platforms.
Unlike legacy satellite hardware, which is often fixed-function and mechanically steered, CesiumAstro’s technology allows communication beams to be shaped, redirected, and optimized entirely through software.
This flexibility has positioned the company at the intersection of commercial scalability and defense-grade reliability, helping it secure contracts with government agencies while also targeting next-generation broadband and connectivity markets.
The Bee Cave expansion reflects the company’s transition from a fast-growing technology developer into a high-volume manufacturer of mission-critical space hardware.
Strategic expansion for Texas satellite production
The new Bee Cave headquarters will anchor the assembly and testing of CesiumAstro’s flagship products, including its Element satellite platform and Vireo multi-beam payloads.
Element is designed as a modular satellite architecture, enabling faster manufacturing cycles and easier upgrades compared to traditional spacecraft designs.
Vireo payloads use active phased-array technology to dynamically allocate bandwidth, allowing satellites to concentrate coverage where demand is highest—whether for military operations, remote broadband access, or resilient communications during emergencies.
CesiumAstro’s expansion follows a June 2024 Series B+ funding round that raised $65 million, led by Trousdale Ventures with participation from the Development Bank of Japan.
The funding accelerated the company’s push toward large-scale production and reinforced its long-term manufacturing strategy in the United States.
To support the Bee Cave project, the Texas Space Commission approved a Space Exploration & Aeronautics Research Fund (SEARF) grant of up to $10 million in May 2025.
The grant provides performance-based reimbursements for specialized equipment and research activities tied to the “Element Satellite Technology Expansion” initiative.
Why Bee Cave? From Land Dispute to Aerospace Hub
While the site selection required local negotiation, Bee Cave ultimately emerged as a strategic fit that extends far beyond available land.
Its proximity to the Austin metropolitan area places CesiumAstro within reach of a deep talent pool spanning RF engineering, embedded software development, digital signal processing, and semiconductor design, as well as research pipelines linked to the University of Texas system.
For state and local officials, the location offers a rare balance of talent density, infrastructure access, and security suitability—making it well-positioned for sensitive aerospace manufacturing without the congestion, logistics strain, or heavy truck traffic associated with traditional industrial zones.
The project also resolves a long-running land-use dispute over “Lot 7” along Highway 71, a parcel previously approved for a large warehouse and distribution center.
That proposal drew significant community opposition over traffic congestion and road safety. In early January 2026, the City of Bee Cave reached a settlement with private developers, allowing CesiumAstro to acquire the property and redirect its use toward a high-technology corporate campus.
Under the redevelopment plan, 76 loading bays intended for heavy logistics will be converted into windows, and 18-wheeler access will be strictly limited to no more than eight escorted trips per month.
Bee Cave Mayor Kara King and city leaders said the aerospace facility will have a markedly lower environmental and traffic impact than the originally proposed warehouse, while delivering far greater economic value.
Beyond land use, the Bee Cave expansion is expected to add approximately 500 high-skill jobs over five years, spanning aerospace systems integration, advanced manufacturing, and software-driven satellite engineering roles that typically command wages well above regional averages.
With more than 300 employees already based across the U.S., U.K., and Japan, the Texas facility will nearly double CesiumAstro’s global workforce.
The site will also include shared testing and integration spaces, creating opportunities for collaboration with smaller aerospace startups and suppliers—an approach aligned with the Texas Space Commission’s broader goal of building a self-sustaining Central Texas space ecosystem.
Operational milestones and project data
The Bee Cave facility is progressing through state-monitored construction and equipment-installation phases tied to SEARF grant requirements.
| Milestone Phase | Timeframe |
|---|---|
| Primary Construction | October 2025 – June 2026 |
| Environmental & Security Systems | November 2025 – August 2026 |
| Fume Extraction & Dust Collection | January 2026 – August 2026 |
| Assembly Workstation Activation | January 2026 – August 2026 |
As of late 2025, the Texas Space Commission reported that $116 million of the $150 million SEARF fund had been allocated across 19 projects statewide.
CesiumAstro’s award ranks among the largest individual grants issued to date, alongside major allocations to Axiom Space and the Aldrin Family Foundation.
CesiumAstro Bee Cave Facility Timeline
Construction of CesiumAstro’s Bee Cave facility will continue through the first half of 2026, with periodic compliance reviews conducted by the Texas Space Commission to ensure grant and security requirements are met.
A separate jury trial related to earlier land-management disputes involving former city officials remains scheduled for February 23, 2026, but does not affect CesiumAstro’s ownership of the site or its development timeline.
By August 2026, the Bee Cave campus is expected to be fully outfitted with specialized satellite manufacturing workstations.
Once operational, the facility will begin domestic production of CesiumAstro’s Element satellite platform, supporting existing and future contracts with NASA and the U.S. Department of Defense.
People Also Ask
What is active phased-array satellite technology?
Active phased-array satellite systems use hundreds or thousands of small antennas controlled electronically to steer communication beams without moving mechanical parts. This allows satellites to operate multiple beams simultaneously, improves reliability, and reduces the risk of mechanical failure in harsh space environments.
Why is CesiumAstro building its headquarters in Bee Cave, Texas?
CesiumAstro selected Bee Cave due to its proximity to Austin’s deep engineering talent pool, access to advanced research infrastructure, and significantly lower traffic and environmental impact compared to a large warehouse or logistics facility.
What role does the Texas Space Commission play in the CesiumAstro project?
The Texas Space Commission awarded CesiumAstro up to $10 million through the Space Exploration & Aeronautics Research Fund (SEARF), while also overseeing compliance and supporting partnerships aligned with state aerospace and national security priorities.
What jobs will CesiumAstro create in Bee Cave?
The Bee Cave facility is expected to create approximately 500 high-skill jobs over five years, including roles in aerospace engineering, embedded software development, satellite manufacturing, systems integration, and corporate operations.