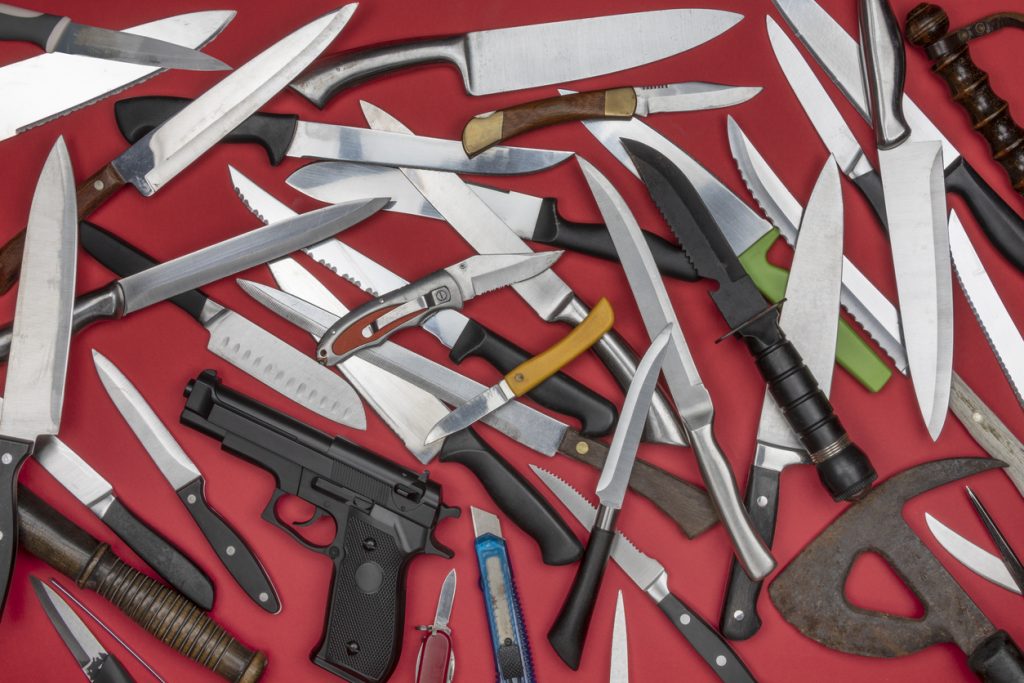
Knife rights vary significantly from state to state in the United States, leading to a complex landscape for knife owners. Understanding the specific laws governing knife ownership, carry, and use in each state is essential for compliance and to ensure personal freedom. From switches and automatic knives to traditional pocket knives, regulations can differ drastically, impacting what individuals can legally possess and carry.
For those navigating these varied laws, knowing the distinctions can prevent legal issues and promote responsible ownership. Some states have relaxed their regulations in recent years, while others maintain strict control over certain types of knives. This blog post will explore the knife laws by state, providing clarity for enthusiasts, collectors, and anyone interested in understanding their rights regarding knives.
The history of knife rights reflects the changing perspectives on personal freedoms and public safety. As society evolved, so did the laws governing knife ownership and carry, influenced by cultural attitudes and notable events.
Knife laws in the United States have been shaped by various historical contexts. In the early 20th century, many states enacted laws regulating or prohibiting specific knife types, often targeting gravity knives and switchblades. These laws stemmed from concerns over juvenile delinquency and crime.
As the years progressed, the landscape began to shift. The 1980s brought increased awareness of personal liberties, leading several states to repeal or amend restrictive knife laws. Advocacy groups emerged, emphasizing that responsible knife ownership should not be hindered by overreaching regulations.
Today, knife laws vary significantly across states, with some embracing more lenient policies that reflect a broader recognition of individual rights.
Federal legislation concerning knives mainly revolves around manufacturing, sales, and import regulations. The Federal Switchblade Act of 1958, for example, restricted the interstate commerce of switchblades, impacting distribution channels.
Over time, several court rulings have clarified the scope of federal knife laws, often siding with personal freedom. Legislation such as the Lawful Commerce in Arms Act does not directly address knives but supports the broader principle of lawful ownership.
As states adapt to changing public sentiment, federal laws remain a crucial backdrop, shaping the landscape within which state-level regulations function. This interplay continues to influence knife rights, making legal clarity essential for owners and enthusiasts.
Knife laws vary significantly from state to state, influenced by factors such as the type of knife, its intended use, and local regulations. Being aware of these laws is crucial for those who carry or use knives for everyday purposes or self-defense.
Knife laws often distinguish between various types of knives, each carrying different regulations. Common categories include:
Specific jurisdictions may impose bans or controls on knives deemed dangerous, such as switchblades or butterfly knives. Understanding these distinctions ensures compliance and helps avoid legal issues.
Knives are commonly classified by their intended use, which affects legal status. Key classifications include:
Legal defenses can differ based on classification. For example, self-defense claims may be more challenging if the knife is considered a weapon rather than a tool. Awareness of classifications assists in navigating the legal landscape effectively.
States impose specific laws regarding how knives can be carried. Common distinctions include:
Failure to adhere to these laws can lead to criminal charges and the need for a criminal defense attorney in places like Amarillo, TX, which can complicate legal matters.
Ownership laws generally permit individuals to buy and own knives, though restrictions apply. Common aspects include:
Violations can result in legal consequences, underscoring the importance of awareness regarding purchasing practices.
Many states pass laws that may override local ordinances. This preemption means:
Understanding these nuances can prevent unintentional violations, especially when engaging with local law enforcement or when in need of legal assistance from a criminal defense attorney.
Knife regulations vary significantly from state to state, influencing how individuals can carry and use knives. Understanding concealed carry laws, open carry provisions, and state preemption rules is essential for compliance.
Concealed carry laws for knives can differ widely across states. Some states require permits to carry a concealed knife, while others do not. For example, in Texas, individuals can legally carry a knife under 5.5 inches without a permit, but concealed carry for larger knives may require specific licenses. Conversely, in states like California, some knives may not be concealed at all.
Individuals should consult a criminal defense attorney in Amarillo, TX for guidance specific to Texas laws. Each state's legal definitions and restrictions may influence permissible blade types and lengths when concealed. Understanding the nuances is crucial to avoid legal complications.
Open carry provisions also vary among states. Most states allow individuals to openly carry knives, but restrictions often apply based on knife types. For example, in Ohio, knives are generally allowed for open carry, as long as they are not classified as prohibited weapons.
In contrast, some states, like Florida, have restrictions on certain types of knives when openly carried. Local regulations may further complicate these provisions, making it essential to verify local laws before carrying openly.
State preemption rules govern local jurisdictions' authority to regulate knives. Some states, such as Arizona, provide preemption, meaning local governments cannot impose stricter regulations than the state. This uniformity helps prevent confusion over local ordinances.
Other states may allow local regulations, creating a patchwork of laws. For instance, in New York, certain cities can enact additional knife laws. Understanding these rules is vital for compliance and avoiding unintended violations. Legal advice can clarify specific obligations under both state and local laws.
Knife rights vary significantly across the United States, with some states adopting restrictive measures while others take a more permissive approach. This section outlines the key differences in regulations and provides illustrative case studies of knife use in various legal contexts.
States categorize their knife laws into two main groups: restrictive and permissive. Restrictive states typically impose strict regulations on knife types, sizes, and carry methods. For instance, in New York, gravity knives and switchblades are banned, severely limiting options for knife owners.
Conversely, permissive states allow broader freedoms for knife ownership and carry. States like Texas permit the open carry of knives over five inches long, while also allowing switchblades. This disparity means individuals must research their state’s specific laws to avoid legal issues. The landscape of knife rights reveals a patchwork of regulations influenced by historical, cultural, and political factors.
Case studies illustrate how knife laws impact day-to-day scenarios. In California, the legal definition of a blade length can affect the charges filed in self-defense cases. A person using a legal knife may face different outcomes than someone with a knife deemed illegal under state law.
On the other hand, in Virginia, a law enforcement interaction involving a folding knife permitted under local laws led to a dismissal of charges in a self-defense case. These examples highlight the practical implications of varying regulations across states, emphasizing the importance of understanding local knife laws for safe and lawful knife ownership.
Understanding the legal terms surrounding knife rights is crucial for compliance and advocacy. Knowledge of statutory language and interpretation can clarify what is permitted in different jurisdictions.
Statutory language varies significantly between states. Each state has its own specific definitions regarding what constitutes a knife, including categories like spring-assisted, switchblade, and folding knives.
For example, some jurisdictions classify knives by blade length or mechanism of action. Common statutory language includes phrases like "dirks," "daggers," and "stilettos." Knife types may be explicitly prohibited or regulated based on local laws.
In many places, specific words can change the legality of a knife. Terms such as "gravity knife" may have different implications depending on the state's definitions. As a result, it is vital to refer to local statutes for exact definitions.
Legal jargon can be complex, making it essential to interpret it accurately. Phrases like "intent to use" can change the context of legality. Understanding the nuances of these terms can impact whether a knife is viewed as a weapon or a tool.
Another critical concept is "constructive possession." This refers to a scenario where an individual may not physically possess a knife but has control over it. Courts often consider such interpretations when determining compliance.
Consulting with a legal professional or reviewing case law may provide clarity on ambiguous terms. Knowledge of local precedents can also help individuals navigate the legal landscape of knife ownership.
Knife ownership pertains to both the rights and responsibilities of individuals who possess knives. Understanding these aspects is essential for proper compliance with varying state regulations.
Knife owners have specific rights that can vary significantly by state. These rights generally include the ability to purchase, carry, and use knives for lawful purposes.
In many states, individuals are permitted to carry knives openly or concealed, though limitations apply. For instance:
Understanding local laws is crucial to avoid potential legal repercussions. Violations can lead to criminal charges, impacting ownership rights.
Legally, knives may be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
In instances of self-defense, the legality of knife use can become complex. It often hinges on factors such as the immediacy of the threat and the proportionality of force applied.
Criminal defense cases involving knives usually assess the context of use. Justifiable use can shield owners from liability, while unlawful use can result in severe penalties. Understanding legal parameters surrounding knife usage is vital for all owners.
Understanding the specific types of knives that are prohibited in various states, along with the penalties for illegal possession, is crucial for knife owners and enthusiasts. Knife laws vary greatly, often resulting in significant legal consequences for violations.
Different states have diverse regulations regarding prohibited knives. Commonly banned types include:
State laws can vary, so it's important for individuals to be informed. For example, Texas allows certain knives but prohibits those over 5.5 inches in specific places. A thorough review of local laws is vital for compliance.
Possessing a prohibited knife can lead to serious criminal charges. Penalties often include:
In states like Florida, individuals may face a third-degree felony for concealed carry of certain knives. Consulting with a criminal defense attorney is advisable in these cases to navigate potential legal repercussions effectively. Legal expertise can help mitigate risks associated with knife possession laws.
Understanding the legal implications of knife crimes is crucial for individuals facing related charges. The role of criminal defense is significant in navigating these matters. Choosing the right criminal defense attorney can also influence the outcome of a case.
Criminal defense encompasses various strategies used to protect a defendant's rights against knife crime allegations. Attorneys analyze the circumstances surrounding the arrest, evidence, and witness accounts. They work to establish defenses, such as self-defense or lack of intent.
Criminal defense professionals in jurisdictions like Amarillo, TX, are familiar with local laws. They can challenge the prosecution's case by questioning the legality of evidence or procedures. Effective defense can lead to reduced charges or even case dismissal, depending on the situation.
Penalties for knife law violations vary significantly by state. Violations can lead to criminal charges, including misdemeanors or felonies, depending on the type of knife and circumstances surrounding the offense. For instance, carrying a concealed dagger may incur harsher penalties than possessing a folding knife in states with relaxed regulations.
Common penalties include:
Individuals in Amarillo, TX may seek guidance from a criminal defense attorney to navigate these complex laws and their associated consequences.
Defending against knife law violations requires an understanding of state laws and the specifics of the case. A criminal defense attorney can provide strategies tailored to the circumstances. Common defenses include:
It is crucial for individuals to work with legal professionals who understand local laws, as the outcome of these cases can hinge on nuances in the law. Seeking an experienced attorney in Amarillo can significantly impact a defendant's chances in court.
Selecting a criminal defense attorney is a vital step for anyone charged with a knife crime. Relevant experience in handling similar cases is essential. An attorney with a strong track record can provide insights into potential outcomes and strategies.
When evaluating attorneys, individuals should consider their communication style and fees. It's crucial to have an attorney who actively listens and prioritizes the client’s interests. Researching online reviews and scheduling consultations can help identify qualified defense attorneys in Amarillo, TX.
Advocating for knife rights involves organized efforts and legal strategies. Various organizations and legal precedents play critical roles in the defense and promotion of these rights across different states.
Numerous organizations work to protect and promote knife rights. The American Knife & Tool Institute (AKTI) is one of the leading groups advocating for the interests of knife owners. They engage in legislative advocacy and education to ensure that knife-related laws are reasonable and fair.
Another key player is Knife Rights, which focuses on eliminating restrictive laws and ensuring lawful ownership and use of knives. This organization actively campaigns against laws that hinder the rights of individuals to carry and use knives for personal, professional, or recreational purposes.
Additionally, local and state groups may also contribute to this movement, providing resources, legal assistance, and community support. Collaborative efforts among these organizations can amplify their impact, leading to more favorable legal environments for knife owners.
Legal precedents have established significant protections for knife ownership. Courts have frequently ruled that knives are not inherently dangerous weapons, emphasizing their utility and everyday use. For instance, in various cases, judges have dismissed charges related to unlawful possession based on the nature of the knives involved, highlighting their common functionality.
Case law also supports an individual's right to carry knives in public. Jurisdictions with 'stand your ground' laws often see courts favor the rights of individuals carrying knives for self-defense. Such legal interpretations reinforce the view that reasonable knife ownership is a protected right.
Criminal defense attorneys often reference these precedents when representing clients charged with knife-related offenses. Successful defenses can rely heavily on emphasizing the utility of knives and their acceptance as everyday tools.
Law enforcement plays a crucial role in the interpretation and enforcement of knife laws across various jurisdictions. Their actions and decisions significantly affect how these laws are applied and understood by the public.
Law enforcement officers often interpret knife laws based on their training, experience, and the specific language of state statutes. They may assess a situation by considering factors such as the intent of the individual carrying the knife, the knife's design, and the context of its use.
For instance, a switchblade or automatic knife may be viewed as illegal in some states, whereas a fixed-blade knife might not be. Officers may also consider the location where the knife is carried, which can impact legality, especially in public spaces or schools.
Enforcement practices can vary widely between states and even between individual officers. Training programs for police may include specific guidelines on how to approach knife-related incidents.
In many cases, police can issue warnings or citations for minor violations rather than making arrests. Legal representation can be critical in these scenarios, particularly for individuals who seek guidance from a criminal defense attorney in Amarillo, TX.
Moreover, understanding local and state regulations can help individuals avoid legal issues, as the consequences of knife-related offenses can range from fines to felony charges.