Hong Kong police arrested three construction-firm employees on suspicion of manslaughter after a fire at a Tai Po housing estate left dozens dead and hundreds unaccounted for, raising urgent questions about building safety and regulatory oversight.
Summary of the Ongoing Investigation
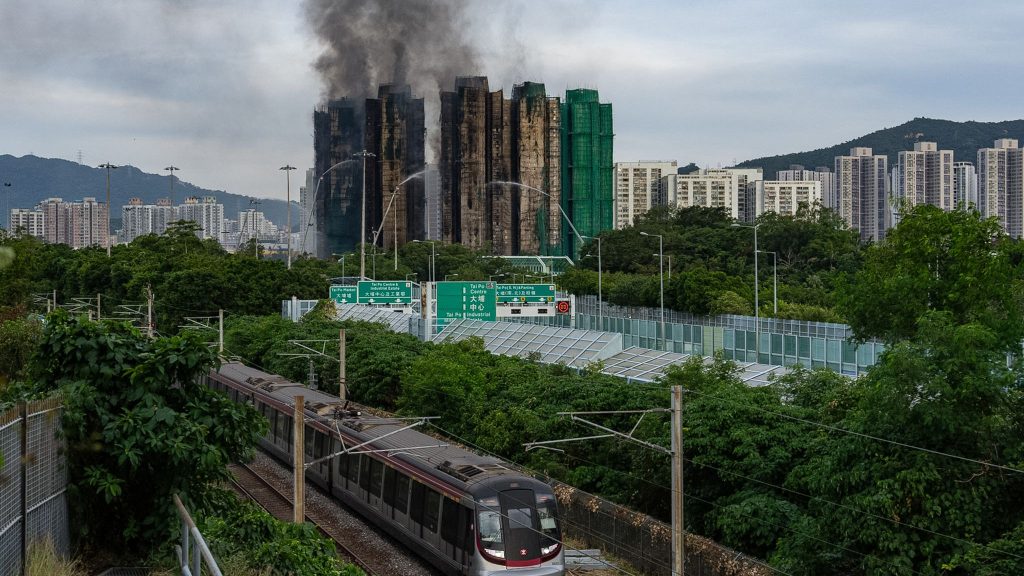
Authorities in Hong Kong have arrested three individuals linked to a construction company after a fire at the Wang Fuk Court housing estate in Tai Po resulted in significant loss of life and widespread structural damage.
The incident occurred on Wednesday afternoon and immediately escalated into one of the region’s most serious residential emergencies. Police say the blaze may have been intensified by bamboo scaffolding and protective mesh installed as part of ongoing maintenance work.
The case now centres on whether construction practices and safety compliance contributed to the spread of the fire.
Hong Kong Police, the Fire Services Department and building-safety regulators are involved in the early stages of the investigation.
The event has drawn concern due to its implications for resident safety, emergency-response capacity and oversight of high-rise maintenance in densely populated urban districts.
What We Know So Far
At least 55 people, including one firefighter, have been confirmed dead following the fire at Wang Fuk Court. Nearly 300 residents remain unaccounted for, while approximately 900 people have been moved to temporary shelters.
Around 45 individuals are in critical condition in hospital.
The housing complex, consisting of eight residential blocks and nearly 2,000 flats, was undergoing renovation at the time of the incident.
Emergency crews reported that four blocks were brought under control by Thursday morning, although flames were still visible in parts of the structure.
Police have stated that preliminary observations suggest the fire may have spread along bamboo scaffolding and mesh sheets that had been installed for maintenance purposes.
Investigators also found sealed windows on one building, which authorities say may have affected evacuation and smoke dispersal patterns.
Three individuals, two directors and an engineering consultant from the construction company responsible for the maintenance work, have been arrested on suspicion of manslaughter. The investigation remains in its early phase.
The Legal Questions Raised
The arrests bring several issues under review, including whether the construction company met statutory safety requirements during renovation work.
Under Hong Kong law, potential offences in such cases may relate to gross negligence, workplace-safety breaches or failures to adhere to building-maintenance standards.
Courts and prosecutors typically examine whether safety controls were reasonable, whether foreseeable risks were mitigated, and whether any conduct materially contributed to the scale of harm.
Building-safety regulations, fire-prevention obligations and contractor-licensing requirements may also come under scrutiny.
The case raises wider questions about the duties of contractors working on occupied high-rise structures and the thresholds at which their actions may trigger criminal liability or regulatory sanction.
Human Rights, Safety and Public-Interest Context
Urban fire safety intersects with core principles of the UN human-rights framework, including the right to life and the state’s duty to ensure safe living environments.
Large-scale residential buildings create systemic risks when safety standards are not adequately enforced.
The fire highlights community-safety concerns in densely populated developments where elderly residents, people with limited mobility and lower-income households may face disproportionate harm during emergencies.
Ensuring accessibility, safe evacuation routes and effective hazard-prevention measures aligns with international public-safety and duty-of-care standards.
The spread of the fire via construction materials also underscores broader issues regarding regulatory oversight of renovation methods and the need for consistent application of safety controls during high-risk maintenance work.
Role of Law Enforcement & Regulators
Police are responsible for determining whether criminal negligence or statutory breaches contributed to the fire’s severity.
Evidence collection typically includes scene forensics, contractor documentation, maintenance logs and witness interviews.
Digital records such as safety-inspection reports, communication between contractors and regulatory submissions may form part of the inquiry.
Fire Services and building-safety authorities generally evaluate the fire’s origin, its propagation and whether building-code compliance was maintained.
Regulators may review scaffolding standards, material approvals and enforcement of phase-out rules for construction fixtures.
Prosecutors become involved once investigators determine whether evidence meets the threshold for formal charges.
International cooperation is unlikely unless cross-border contractual or supply-chain issues emerge.
Risks, Implications & Public Impact
The incident has implications for public safety in high-density residential areas where renovation activity is common. Failures in safety compliance can heighten community concern about evacuation reliability and structural integrity during emergencies.
The case also affects public trust in regulatory oversight, particularly concerning the phase-out of certain construction materials and the monitoring of contractors working on occupied buildings.
Platforms hosting videos or public updates may face questions about the accuracy and timing of shared information during fast-moving emergencies.
The scale of the fire places attention on safeguarding obligations toward vulnerable residents and may prompt a broader policy review of maintenance practices in older residential estates.
Key Questions People Are Asking
How did authorities determine suspicion of manslaughter?
Police stated that findings at the scene, including sealed windows and material installation patterns, indicated possible gross negligence by responsible parties. Under Hong Kong law, suspicion may arise when conduct appears to have created foreseeable risk leading to serious harm.
Why did scaffolding play a role in the fire’s spread?
Emergency officials reported that bamboo scaffolding and mesh sheets can act as conduits for flames in certain conditions. Investigators examine whether permitted materials were used and whether safety protocols were followed during installation.
What standards apply to maintenance work on occupied residential towers?
Contractors are subject to building regulations, safety codes and industry guidelines governing scaffolding, fire-break systems and debris-management controls. Authorities assess whether these were met at the time of the incident.
What support is provided to displaced residents?
Local authorities typically coordinate temporary shelters, medical assistance and documentation services. This process is separate from the criminal investigation but operates alongside it to ensure resident welfare.
How does this incident compare to previous major fires in Hong Kong?
The current death toll exceeds that of the 1996 Kowloon blaze, which led to significant regulatory reforms. Comparisons are being made to understand whether earlier safety improvements were consistently applied.
Next Steps and Legal Implications
Investigators will continue structural examinations, forensic sampling and review of contractor records, while authorities analyse safety documentation, renovation permits and communications between the construction firm and regulatory bodies.
Prosecutors will determine whether the evidence meets charging thresholds for manslaughter or related offences, and building-safety regulators may issue interim findings or notices as the review progresses.
Emergency services will keep accounting for missing residents and supporting recovery efforts, with further updates dependent on confirmed developments.
The incident has initiated a criminal investigation focused on safety compliance, contractor obligations and regulatory oversight in occupied high-rise buildings, and its findings may shape future maintenance standards, risk-management practices and public-safety expectations.
Ensuring accountability within established legal processes will be central to maintaining public confidence and clarifying the responsibilities of those involved.