Distracted Driving Cases in California: The Role of Cell Phones
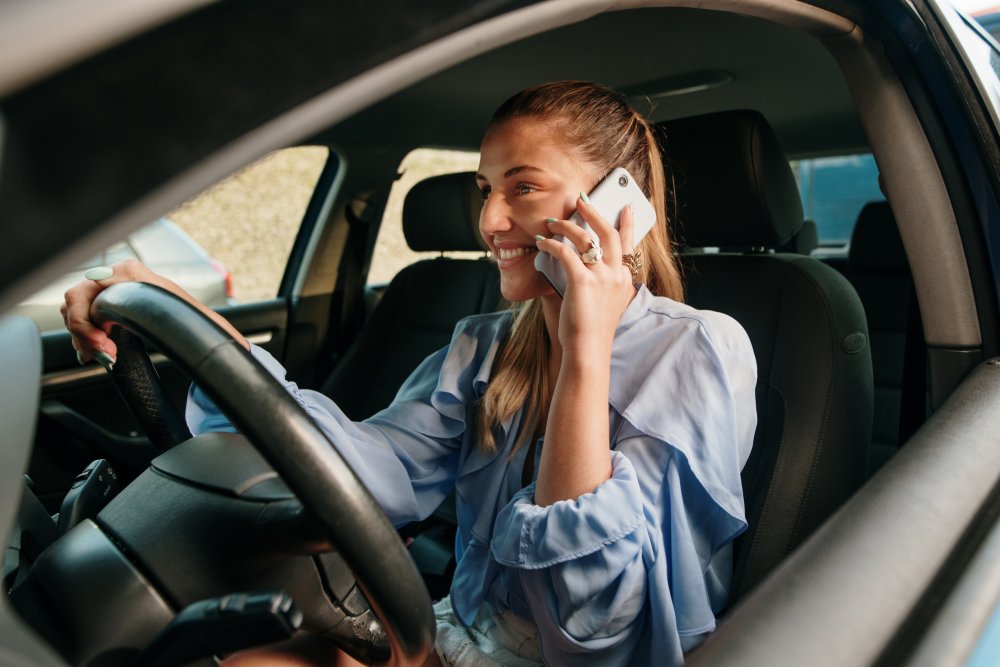
Distracted driving has become a public safety crisis in California, with the use of cell phones at the center of the issue.
What began as a modern convenience has morphed into a dangerous habit, leading to a significant number of accidents, severe injuries, and tragic fatalities on the state's roadways.
Understanding the intricate legal framework surrounding these incidents is essential for both victims seeking justice and drivers aiming to navigate the road responsibly and avoid life-altering consequences.
The Legal Landscape: California's Hands-Free Laws
California has been a leader in enacting strict laws to combat distracted driving, specifically targeting the use of electronic devices.
The state's primary legal tool is the "hands-free" law, codified in the California Vehicle Code.
Specifically, Vehicle Code Section 23123 prohibits drivers from operating a motor vehicle while using a wireless telephone unless it is configured for hands-free use.
A separate, but related, law, Vehicle Code Section 23123.5, makes it illegal to write, send, or read text-based communications while driving.
These laws are not mere suggestions; they are primary offenses, meaning a law enforcement officer can pull a driver over and issue a citation solely for a violation, without any other traffic infraction.
The legislative history of these laws highlights the state's evolving response to the threat.
California first banned handheld cell phone use in 2008. In 2017, the law was strengthened to clarify that a driver can only use a phone if it is securely mounted on the dashboard or windshield, and can be operated with a single swipe or tap.
This move aimed to eliminate the ambiguity that allowed drivers to claim they were merely "using GPS" or "checking the time."
The fines for a first offense are relatively low, but with additional court fees and surcharges, they can quickly escalate.
More importantly, these violations result in points on a driver's record, which can lead to higher insurance rates and, in some cases, license suspension for repeat offenders.
The Perilous Impact of Cell Phone Distraction
The dangers of cell phone use extend far beyond a simple moment of inattention. The act of using a phone while driving combines three distinct types of distraction, making it exceptionally dangerous:
- Manual Distraction: Taking your hands off the steering wheel to hold the device.
- Visual Distraction: Taking your eyes off the road to look at the screen.
- Cognitive Distraction: Taking your mind off the task of driving to process information from the call or message.
This multi-faceted distraction impairs a driver's ability to react to hazards, maintain a consistent speed, and stay within their lane.
According to the California Office of Traffic Safety, cell phone use remains the single biggest distraction for drivers, and it is a leading cause of crashes, especially among younger drivers.
Statistics show that the number of distracted driving fatalities has fluctuated, but the overall trend remains a serious concern for public safety.
The California DMV's Driver Handbook also reinforces this by stating that driving safely requires your full attention and that any non-driving activity is a potential distraction.
Proving Negligence: The Crucial Role of Evidence
In California, a "fault" state, a person injured by a distracted driver must prove that the other driver was negligent. Proving this negligence is the cornerstone of any personal injury claim.
In cases involving cell phone use, the burden of proof often relies on compelling evidence that ties the driver's device use directly to the crash.
- Cell Phone Records: This is often the most powerful form of evidence. An attorney can subpoena a driver's cell phone records to obtain a log of calls, text messages, and data usage at the time of the accident. These records can reveal if a call was in progress or if a text was sent or received just seconds before the collision.
- Eyewitness Testimony: A witness who saw the at-fault driver looking down at their lap or holding a phone can provide critical testimony.
- Police Reports: If a law enforcement officer observes signs of distraction or finds a cell phone in use at the scene, this information will be noted in the official police report, which serves as a key piece of evidence.
- Dashcam or Surveillance Footage: Footage from other vehicles, nearby businesses, or traffic cameras can visually confirm that a driver was using their phone at the time of the crash.
In addition to proving negligence, this evidence is vital in civil lawsuits to establish a driver's conscious disregard for public safety.
This can allow a victim to seek punitive damages, which are designed not just to compensate for a loss, but to punish the defendant and deter similar behavior in the future.
Civil and Criminal Remedies for Victims
Victims of distracted driving accidents have multiple legal avenues to pursue justice and compensation.
Civil Remedies:
- California Vehicle & Traffic Accident Claims: This is the primary civil claim for any vehicle collision. A claim for damages is filed against the at-fault driver and their insurance company.
- California Car Accident Laws: Fault, Insurance, and Compensation: California's comparative fault system is critical here. Even if a victim is found to be partially at fault for an accident (e.g., they were slightly speeding), they can still recover damages, but the amount will be reduced by their percentage of fault. This is why proving the other driver was distracted is so important—it shifts the majority, if not all, of the fault to them.
- Motorcycle Accidents in California: Legal Rights of Riders: Motorcyclists are often difficult for inattentive drivers to see, making them disproportionately vulnerable to distracted driving. Proving the driver was on their phone can be essential for a rider to recover from severe injuries.
- Pedestrian Accidents in California: What Victims Should Know: A pedestrian hit by a distracted driver can face life-altering injuries. Their legal claim can be strengthened immensely by evidence of the driver's cell phone use.
- Bicycle Accident Lawsuits in California: Shared Road Responsibilities: Similar to pedestrians and motorcyclists, cyclists are at high risk. An article about distracted driving should include images of the kinds of dangers and the distracted drivers. Shared road responsibility means a cyclist has a duty of care, but a distracted driver's negligence will almost certainly outweigh any minor fault on the cyclist's part.
- Truck Accident Claims in California: Complex Liability Issues: Distracted driving in a commercial truck can be catastrophic. Proving that the trucker was on their phone not only holds the driver accountable but can also extend liability to their employer if the phone use was work-related.
- Rideshare Accidents: Uber & Lyft Liability in California: If an Uber or Lyft driver is distracted by a cell phone—whether it's their personal phone or the rideshare app itself—the company's extensive insurance policies may be triggered. This adds a layer of complexity to the claim, often requiring a skilled attorney to navigate.
- Drunk Driving Accident Lawsuits in California: While legally distinct, the legal community and juries often view egregious distracted driving with the same level of reckless disregard as drunk driving. Victims can pursue similar punitive damages in both types of cases.
- Hit-and-Run Accidents in California: Civil and Criminal Remedies: A distracted driver may panic after an accident and flee the scene. While this adds a criminal element, a civil lawsuit can still be filed against the driver once they are identified.
- Public Transportation Accidents: Suing a Government Agency in California: If a driver of a public bus or train is distracted by a cell phone, a victim would have to sue the government agency that employs them. This involves a different and often more complex legal process with strict timelines and notice requirements.
Criminal Penalties:
While most cell phone violations are minor traffic infractions, they can become serious criminal offenses if they result in injury or death.
Depending on the level of negligence, a distracted driver could be charged with a felony, such as vehicular manslaughter.
A criminal conviction can also have a profound impact on a civil lawsuit, as it serves as powerful evidence of the driver's gross negligence.
The Growing Trend
As the dangers of distracted driving have become more widely known, juries have shown a willingness to award substantial damages to victims.
This is especially true when evidence of cell phone use is undeniable. Recent high-profile cases have resulted in multi-million dollar verdicts and settlements, sending a clear message that courts will not tolerate this behavior.
A landmark case in California saw a jury award over $140 million to a man who suffered a traumatic brain injury after being struck by a distracted driver. Such verdicts serve as a powerful deterrent and highlight the critical importance of being properly insured.
The Path to a Safer California
The ubiquity of cell phones has created a dangerous new era on California's roads.
The legal system, through a combination of strict laws and a robust civil and criminal framework, is working to hold negligent drivers accountable.
For every driver, the message is simple and urgent: put the phone away. For every potential victim, knowing the legal recourse and the power of evidence is the first step toward rebuilding their lives.
As a society, we must continue to educate and enforce these laws to make our roads safe for everyone, from pedestrians and cyclists to motorcyclists and other drivers. The cost of a text, a call, or a scroll is simply too high.
People Also Ask (PAA)
What is California's law on cell phone use while driving?
California law makes it illegal for a driver to operate a motor vehicle while holding a cell phone or any other portable electronic device. Using a phone for a call or GPS is only permitted if the device is securely mounted and can be operated with a single swipe or tap.
How can you prove a driver was distracted by their phone?
Proving a driver was distracted often relies on several types of evidence, including cell phone records (showing calls or texts at the time of the crash), eyewitness testimony, police reports, and any available dashcam or surveillance footage.
What are the penalties for distracted driving in California?
A first-time offense for distracted driving typically results in a fine. However, with additional court fees and surcharges, the total cost can be significantly higher. These violations also add points to a driver's record, which can lead to increased car insurance rates.
Does California's law on distracted driving apply to all vehicles?
Yes, California's "hands-free" and anti-texting laws apply to all drivers of motor vehicles, including motorcycles, commercial trucks, and rideshare vehicles.